Azure Login Portal: 7 Ultimate Tips for Secure Access
Accessing the Azure login portal is the first step to managing your cloud resources with confidence and control. Whether you’re an IT admin, developer, or business owner, mastering secure and efficient login practices is essential in today’s digital landscape.
Understanding the Azure Login Portal

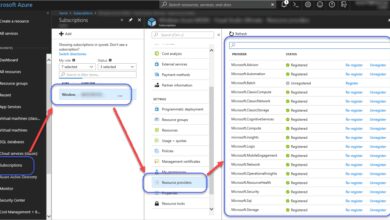
The Azure login portal is the primary gateway to Microsoft Azure, a comprehensive cloud computing platform offering services like virtual machines, databases, AI tools, and more. When users navigate to portal.azure.com, they are directed to the official Azure login portal where authentication is required to access their cloud environment.
What Is the Azure Login Portal?
The Azure login portal is not just a simple sign-in page; it’s a secure entry point integrated with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory). It enables identity verification, role-based access control, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect sensitive data and infrastructure.
- It serves as the central hub for managing subscriptions, resources, and user permissions.
- Users can access it from any device with an internet connection and a supported browser.
- The portal supports single sign-on (SSO) for organizations using federated identity providers.
How Authentication Works in the Azure Login Portal
Authentication in the Azure login portal relies on Microsoft Entra ID, which verifies user credentials through various methods including passwords, security keys, biometrics, and MFA. Once authenticated, users are granted access based on their assigned roles and policies.
“The Azure login portal is designed to balance usability and security, ensuring only authorized individuals can manage critical cloud assets.” — Microsoft Cloud Security Guidelines
Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing the Azure Login Portal
Logging into the Azure portal is straightforward, but understanding each step ensures a smooth and secure experience. This section walks you through the process from start to finish.
Navigating to the Official Azure Login Portal
To begin, open your preferred web browser and go to https://portal.azure.com. Always ensure you’re on the legitimate Microsoft site to avoid phishing attempts. Look for the padlock icon and “microsoft.com” in the URL bar.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links from emails or messages claiming to lead to the Azure login portal.
- Bookmark the official URL for quick and safe access.
- Use private/incognito mode if logging in from a shared or public computer.
Entering Your Credentials
On the Azure login portal page, enter your work or school account email address (e.g., user@company.com). Personal Microsoft accounts (like @outlook.com) may also be used if granted access to Azure resources.
- If your organization uses conditional access policies, additional verification steps will appear after entering your password.
- Ensure Caps Lock is off and your keyboard layout is correct to avoid login errors.
- Use a password manager to store and autofill complex passwords securely.
Completing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
After entering your password, the Azure login portal may prompt you for a second form of verification. This could include:
- A notification via the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- A phone call or SMS code.
- A hardware security key or FIDO2 token.
Completing MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised.
Common Issues When Using the Azure Login Portal
Despite its reliability, users occasionally face challenges when trying to log in to the Azure login portal. Identifying and resolving these issues promptly is crucial for maintaining productivity.
Forgot Password or Locked Account
One of the most frequent issues is forgetting your password or getting locked out due to multiple failed attempts. The Azure login portal provides a “Forgot password?” link that guides users through a recovery process.
- Recovery options depend on your organization’s self-service password reset (SSPR) configuration.
- Admins can reset passwords via the Microsoft Entra admin center.
- Ensure your contact information (email, phone) is up to date to facilitate recovery.
Multi-Factor Authentication Failures
MFA failures can occur due to expired tokens, lost devices, or network issues. If you’re unable to complete MFA:
- Try alternative methods like phone calls or backup codes if configured.
- Contact your IT administrator to approve a temporary bypass or re-register your device.
- Use the MFA setup page to manage your authentication methods.
Browser and Compatibility Issues
Some browsers may not fully support the Azure login portal, leading to loading errors or broken functionality.
- Use supported browsers: Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Firefox, or Safari.
- Clear cache and cookies if the login page appears frozen or unresponsive.
- Disable browser extensions that might interfere with scripts on the Azure login portal.
Enhancing Security on the Azure Login Portal
Security is paramount when accessing cloud environments. The Azure login portal offers several advanced features to strengthen authentication and prevent breaches.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is one of the most effective ways to secure your Azure login portal access. It requires users to provide two or more verification factors, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access.
- Admins should enforce MFA for all users, especially those with elevated privileges.
- Use the Microsoft Authenticator app for push notifications and time-based one-time passwords (TOTP).
- Configure MFA registration policies to ensure all users complete setup during their next sign-in.
Implementing Conditional Access Policies
Conditional Access in Microsoft Entra ID allows organizations to define rules that control how and when users can access the Azure login portal.
- Restrict access based on user location, device compliance, or sign-in risk level.
- Require MFA for users accessing from untrusted networks.
- Block legacy authentication protocols that don’t support modern security standards.
“Conditional Access turns the Azure login portal into a dynamic security checkpoint, adapting to real-time risk signals.” — Microsoft Security Blog
Using Identity Protection and Risk-Based Policies
Azure AD Identity Protection monitors sign-in activities and detects anomalies such as impossible travel, unfamiliar locations, or leaked credentials.
- Set up risk-based policies to automatically prompt high-risk users for MFA or block access.
- Review risky sign-ins in the Microsoft Entra admin center.
- Integrate with Microsoft Defender for Cloud for enhanced threat detection.
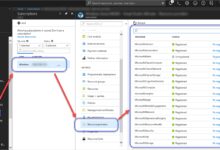
Managing User Roles and Permissions via the Azure Login Portal
Once logged in, administrators can manage who has access to what within the Azure environment. Proper role assignment is key to maintaining security and operational efficiency.
Understanding Built-in Roles in Azure
Azure provides several predefined roles that simplify permission management:
- Owner: Full access to all resources and can delegate access to others.
- Contributor: Can create and manage all types of Azure resources but cannot grant access to others.
- Reader: View existing resources but cannot make changes.
- User Access Administrator: Manage user access to Azure resources.
These roles can be assigned at the subscription, resource group, or individual resource level.
Creating Custom Roles for Specific Needs
For organizations with unique requirements, Azure allows the creation of custom roles with granular permissions.
- Define actions, not actions, and assignable scopes using JSON templates.
- Test custom roles in a non-production environment before deployment.
- Audit role usage regularly to ensure compliance and minimize over-privileged accounts.
Best Practices for Role Assignment
Following the principle of least privilege is essential when assigning roles through the Azure login portal.
- Grant only the minimum permissions necessary for a user to perform their job.
- Use Just-In-Time (JIT) access via Azure Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for temporary elevated access.
- Regularly review access assignments and remove unnecessary permissions.
Using the Azure Login Portal Across Devices and Platforms
The Azure login portal is accessible from various devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones. While the full experience is optimized for desktop browsers, mobile access is possible with some limitations.
Desktop vs. Mobile Experience
On desktop, users enjoy a full-featured interface with drag-and-drop functionality, detailed dashboards, and comprehensive management tools.
- Mobile browsers provide read-only access to key resources and alerts.
- The Microsoft Azure app (available on iOS and Android) allows basic monitoring and management tasks.
- Complex operations like deploying templates or configuring networks are best done on desktop.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration
Organizations can integrate the Azure login portal with enterprise identity providers like Okta, Ping Identity, or on-premises Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS).
- SSO reduces password fatigue and improves user experience.
- It centralizes identity management and enhances security through centralized policy enforcement.
- Configure SSO via the Microsoft Entra admin center under Enterprise Applications.
Using Guest Accounts and External Identities
The Azure login portal supports collaboration with external users through Azure AD B2B (Business-to-Business) functionality.
- Invite partners, vendors, or contractors by email to access specific resources.
- Guest users sign in using their own credentials from their home directory.
- Admins can apply the same security policies (MFA, Conditional Access) to guest accounts.
Advanced Features of the Azure Login Portal
Beyond basic login and navigation, the Azure login portal offers powerful tools for automation, monitoring, and governance.
Accessing Azure CLI and PowerShell from the Portal
The Azure login portal includes an embedded Cloud Shell that allows users to run Azure CLI or PowerShell commands directly in the browser.
- No installation required—Cloud Shell runs in a sandboxed environment.
- Persistent storage is available via an Azure Files share.
- Useful for scripting, automation, and troubleshooting without leaving the portal.
Monitoring Sign-Ins and Audit Logs
Security teams can audit user activity by reviewing sign-in logs and audit logs in the Microsoft Entra portal.
- Track successful and failed login attempts to the Azure login portal.
- Identify unusual patterns or potential breaches.
- Export logs to Azure Monitor or Sentinel for long-term analysis and alerting.
Customizing the Dashboard for Efficiency
Users can personalize their Azure login portal dashboard by pinning frequently used resources, creating custom views, and setting up alerts.
- Add tiles for VMs, databases, or cost management tools.
- Share dashboards with team members for collaborative monitoring.
- Use the “Favorites” feature to quickly access commonly used services.
Troubleshooting and Support Resources for the Azure Login Portal
Even with robust systems, issues can arise. Knowing where to find help is crucial for minimizing downtime.
Official Microsoft Documentation and Support
Microsoft provides extensive documentation for the Azure login portal and related services.
- Visit Microsoft Learn for guides on security, MFA, and identity management.
- Access the Azure Status page to check for service outages affecting the login portal.
- Open a support ticket via the Azure portal if internal troubleshooting fails.
Community Forums and Expert Help
The Azure community is active and helpful, offering peer support through forums and Q&A platforms.
- Post questions on Microsoft Q&A to get answers from MVPs and Microsoft engineers.
- Join Reddit communities like r/Azure or Stack Overflow for real-world troubleshooting tips.
- Attend webinars or Microsoft Ignite sessions for expert insights.
Using Azure Advisor for Optimization
Azure Advisor is a built-in tool that provides personalized recommendations for improving security, performance, and cost efficiency.
- It may suggest enabling MFA or removing unused accounts.
- Follow its guidance to harden your Azure login portal security posture.
- Set up email alerts for critical recommendations.
How do I reset my password for the Azure login portal?
If you’ve forgotten your password, click the “Forgot password?” link on the Azure login portal. You’ll be guided through a recovery process that may involve answering security questions, receiving a code via email or SMS, or using the Microsoft Authenticator app. If self-service password reset (SSPR) is enabled by your organization, you can reset it immediately. Otherwise, contact your IT administrator.
Why am I unable to log in to the Azure login portal?
Common reasons include incorrect credentials, expired passwords, disabled accounts, MFA setup issues, or browser compatibility problems. Check your internet connection, ensure you’re using the correct URL (portal.azure.com), and try a different browser. If the issue persists, consult your administrator or check the Azure Status page for outages.
Can I use a personal Microsoft account to access the Azure login portal?
Yes, but only if your Azure subscription or resource has been explicitly shared with your personal account. Most enterprise environments require a work or school account (managed by Microsoft Entra ID). Personal accounts are typically used for free trials or individual developer subscriptions.
What should I do if MFA is not working on the Azure login portal?
If MFA fails, try alternative methods like phone calls, SMS, or backup codes. If none work, use the MFA setup recovery page or contact your administrator to reset your authentication methods. Ensure your registered devices are functional and connected to the internet.
Is the Azure login portal secure?
Yes, the Azure login portal is built with enterprise-grade security, including encryption, MFA, Conditional Access, and identity protection. However, its security also depends on user practices—such as using strong passwords and enabling MFA. Organizations should enforce security policies to maximize protection.
Mastering the Azure login portal is essential for anyone managing cloud resources. From secure authentication and role management to troubleshooting and optimization, this guide has covered the critical aspects of accessing and using the portal effectively. By following best practices in security, permissions, and monitoring, you can ensure a smooth and protected experience every time you log in. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced admin, continuous learning and proactive management will keep your Azure environment secure and efficient.
Further Reading: